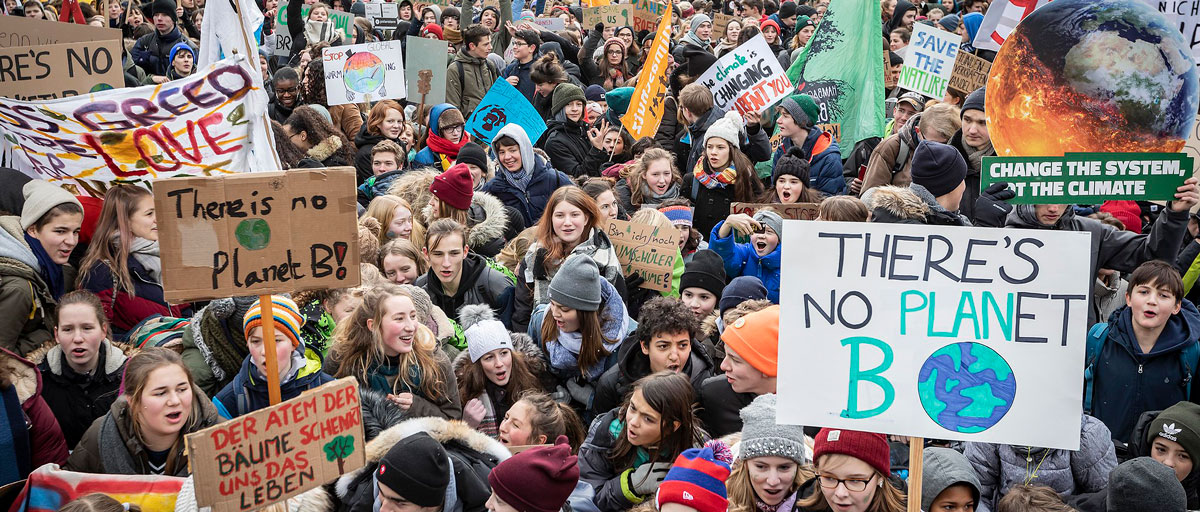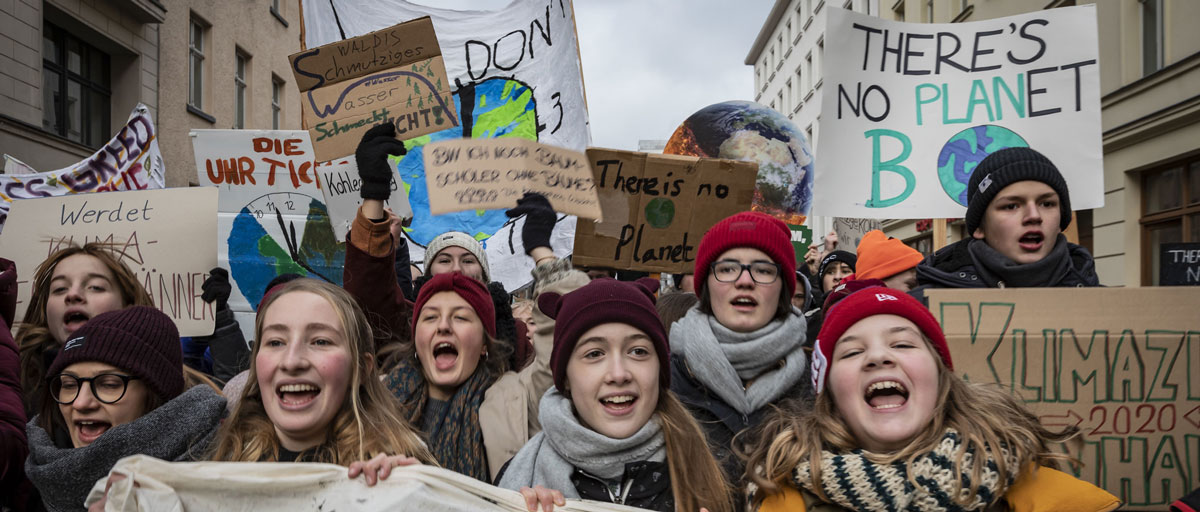Bildtext får vara max två rader text. Hela texten ska högerjusteras om den bara ska innehålla fotobyline! Photo: B. Christensen/Azote
Social change
Social tipping mechanisms could spark societal change
- Reaching the Paris climate agreement’s goals requires a world-wide decarbonization by 2050
- Concrete interventions that set off positive social tipping dynamics can trigger this global transformation
- More research is needed to further examine these interventions
Changes in opinions and behaviour can trigger a global sustainability transformation
CONTAGIOUS CHANGE: Reaching the Paris climate agreement’s goals requires a world-wide transformation to carbon-neutral societies within the next 30 years. That may sound overwhelming, but in today’s tightly networked world changes in people’s opinions and behaviour can quickly turn into a global transformation.
In a study published in Proceeding of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, centre researchers Jonathan Donges and Johan Rockström evaluate the potential for such social dynamics to speed up and disseminate new technologies, norms and behaviours.
The researchers looked for what experts in the research community call social tipping elements, or critical interventions that could set a change in motion.
One example is the #FridaysForFuture movement where school children have gone on strike to bring attention to the climate crisis. The movement has spread across the world and the ripples it is creating could impact on people’s norms, beliefs and behaviours, with possible effects on individual consumption as well as policy and infrastructure development.
Social tipping dynamic is much like the contagious spread of behavior or opinions in social networks, resembling the spread of epidemics. A small change can lead to larger advancements on the larger scale.
Jonathan Donges, co-lead author
Six areas to boost change
For such contagious change to happen, certain structural improvements, or “interventions”, must occur too. Specifically, the authors identified six possible interventions:
1. removing fossil fuel subsidies and incentivizing distributed energy generation
2. building carbon-neutral cities
3. divestments from assets linked to fossil fuels
4. revealing the moral implications of fossil fuels
5. strengthened climate education and engagement
6. greenhouse gas emissions information disclosure
The authors stress that this is not necessarily comprise a comprehensive list of “silver bullet” solutions but rather an initial selection that can help in developing more refined socio-economic rapid transformation pathways.
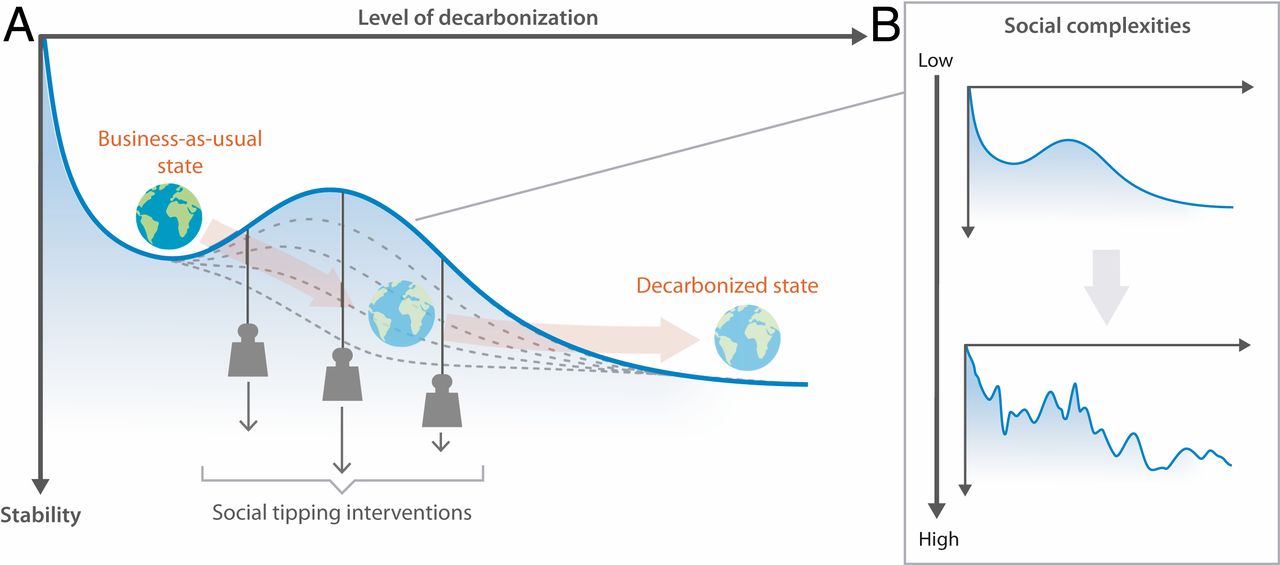
The concept of decarbonization transformation as social tipping dynamics. As illustrated in A by an abstract stability landscape (155), the world’s socioeconomic system today is trapped in a valley where it still depends heavily on burning fossil fuels, leading to high rates of greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions. STIs have the potential to erode the barrier through triggering social tipping dynamics in different sectors. Click on illustration to access scientific study.
Methodology
The primary data collection tool was an online expert survey that was sent to over 1000 international experts through a private message or addressed through mailing lists of organizations in the field of climate change and sustainability. The online survey was completed by 133 experts. In addition, a selected group of 17 experts took part in an in-depth workshop that focused on choosing the top candidates for social tipping elements instrumental for decarbonization by 2050 and assessing the interactions between the social tipping elements. Finally, the co-authors carried out a literature review on the top candidates for social tipping elements selected at the workshop, following the literature review guidelines.
Otto, I.M., Donges, J.F., Cremades, R., Bhowmik, A., Hewitt, R.J. et.al. 2020. Social tipping dynamics for stabilizing Earth’s climate by 2050. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, Jan 2020, 201900577; DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1900577117